Abstract
Chromosomal translocations are a common cytogenetic aberration in acute leukemia, which frequently generate fusion proteins with oncogenic properties. We have previously studied the immune evasion mechanisms of two common oncogenic fusion proteins in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), PML-RARA and AML1-ETO. We investigated, in particular, the activity of natural killer (NK) cells, which are part of the innate immune system and play a significant role in eliminating leukemic cells. We found that both oncogenic fusion proteins downregulate the expression of CD48, a ligand of the NK cell activating receptor 2B4, to escape NK cell-mediated recognition of the tumor cells.
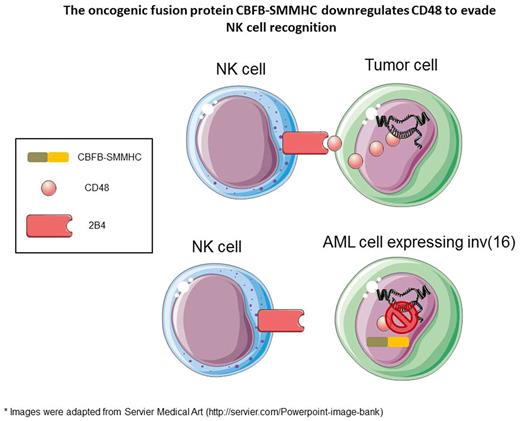
In the current study we tested the possibility that other oncogenic fusion proteins are also able to evade NK cell recognition. To this aim we cloned several leukemic fusion proteins into lentiviral vectors and expressed them in U937 cells, which are commonly used to express leukemic fusion proteins. The leukemic fusion proteins included MLL-AF4, NUP98-HOXA9, DEK-NUP98 and CBFB-SMMHC. By using flow cytometry, we examined the effect of these fusion proteins on the expression of several NK cell ligands. CBFB-SMMHC was the only fusion protein which downregulated the expression of CD48.
Next, we tested the functional significance of the downregulation of CD48 by CBFB-SMMHC by performing cytotoxicity assays with NK cells. We first used the NK cell line YTS eco since the cytotoxicity of these cells is mainly dependent on the 2B4-CD48 interaction. We found that cells which express CBFB-SMMHC were killed significantly less than the control cells, and that this reduced killing was due to CD48 downregulation. We also tested the killing of CBFB-SMMHC expressing cells by primary bulk NK cells and found that cells which express this fusion protein were killed significantly less.
Mechanistically we show that overexpression of CBFB-SMMHC reduces the mRNA levels of CD48. Additionally, we tested whether treatment with HDAC inhibitors (HDACi) can reverse the downregulation of CD48 by CBFB-SMMHC. We treated cells which express CBFB-SMMHC with various HDACi and examined the effect of this treatment on the expression of CD48. Two specific class I HDACi, mocetinostat and entinostat, upregulated the expression of CD48 in cells which express this fusion protein.
Taken together we show that modulation of CD48 expression is an immune evasion mechanism, which is specific to core binding factor (CBF) proteins (AML1-ETO and CBFB-SMMHC) and PML-RARA. Although the three fusion proteins which we found to down-regulate the expression of CD48 are associated with better prognosis in AML, about 30% of CBF-AML patients eventually relapse. Based on our findings we suggest that down-regulation of CD48 by these fusion proteins, which leads to NK cell immune evasion, contributes to the persistence of residual disease in these subtypes of leukemia and eventually to a clinical relapse. Finally, we propose that NK cell based therapies (i.e., NK cell infusion) or class I HDACi could be potential adjunctive therapies for CBF-AML or APL.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal